Containment through filter systems – employee protection in the pharmaceutical industry: In many branches of industry, dust is a type of hazardous substance due to its composition and is therefore a major problem. Particularly in the pharmaceutical industry, the composition of dust and daily dust exposure for employees is an important issue, because the particles generated during production are in the air at the workplace. Without further protective measures, they can thus enter the respiratory tract of employees, where they may have serious health consequences. Therefore, employee protection – e.g. in the environment of tablet production – is particularly important, since on the one hand the self-cleaning mechanism of the respiratory tract can no longer cope with or remove an excessive amount of dust on its own, and on the other hand the active ingredients used can become a hazard if employees are exposed to them over a longer period of time.
Learn how to protect your employees from hazardous dusts in our blog article.
Containment by filter systems – effective employee protection in the pharmaceutical industry
During the production of medications, it is important to remove the swirled particles from the air so that they do not come into contact with the employees. Various measures are in place to protect employees in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products. In the pharmaceutical environment, this form of employee protection is called containment.
When selecting a suitable containment measure, the production process plays an important role:
- There are cleanroom solutions whose goal is not to allow dust to escape into the ambient air.
- Separators and airlocks installed within the production lines ensure that the dust generated remains where it is created and is not spread further.
- To create a safe environment, the air can also be cleaned.
An effective solution here are special filter systems or dust extraction systems, which use special filter technology to remove even the finest particles from the air and thus create the purest air.
The choice of dust filtering equipment is wide. For the tablet production processes presented here, dedusting systems are suitable which, with a suitable dust collection system, ensure that the particles are collected shortly after swirling by means of a suction effect and separated in the filter system via a piping system. Active exhaust air dedusters are used, for example, to prevent dust-laden air from escaping into the environment during the production of powder granules. These dedusting units are often installed at the end of the process, take in the so-called raw gas (=dust-laden air) and separate the dust particles from the air flow.
The primary purpose of the dust collection system is therefore to safely remove the dust from the production area and thus from the direct danger zone of the employees and their health. This underlines the importance of employee protection in the industry, where safety in the workplace is a top priority. It is therefore essential to precisely define the following five criteria for the selection of such equipment and to select the appropriate protective measures for the defined process and with the described substances in order to ensure employee protection.
1. classification of occupational exposure to dust (OEL)
Not all dust is created equal
The dust in the pharmaceutical industry is composed of the components of the tablets. In addition to the actual active ingredient, these include other components that affect the properties of the tablets or drugs. Depending on the constituent, the hazard to employees can vary: Not only the type of substance and its components, but also the dose, or how long the employee is exposed to this substance during daily work, are decisive for the health risk to employees. For this purpose, a workplace limit value is defined for each substance, the so-called OEL (Occupational Exposure Limit). This indicates how much of the substance may be contained in one cubic meter of air so that the employee is not exposed to any health hazards.
The basis for the OEL is the “NOEL = No-Observable Effect Level”. It indicates the daily dose at which a critical effect is just prevented. Other factors are taken into account in addition to this daily dose, such as:
- The adaptation of animal to human data,
- different sensitivities of people,
- the duration of the studies,
- the severity of the effects or
- if significant effects occurred despite compliance.
This results in the “ADE=Acceptable Daily (Worker) Exposure”. This is the daily tolerated dose, which – based on a day’s breathing air – gives the OEL.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the studies of the manufacturers of these substances serve as a source for the evaluation of substances.
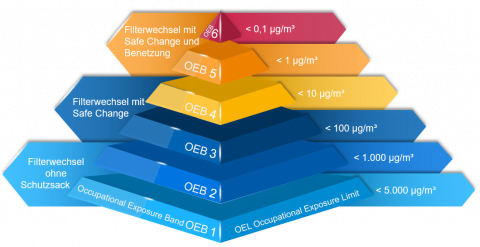
2. assignment of the plants to OEB levels (requirements of the pharmaceutical industry).
If not enough information is available for a substance to determine the OEL and thus assess the hazard, classification systems are used. These are used to assign the substance to a hazard category (also called a class or band). One common system is that of “Occupational Exposure Bands,” or OEBs. The lowest level applies to the least active substances, i.e. the substances that are not so dangerous to harmless. The highest level again applies to the most active substances, i.e. substances for which even a small amount of material is sufficient to pose a major hazard.
This categorization is contrasted with a classification of the production equipment to be used: Depending on the design, different amounts of dust can escape during the production process. Depending on the classification of the substance, the properties of the equipment must then be selected. This means that, for example, for less active substances in category OEB1, facilities with little to no containment measures can be chosen to protect employees because the substance poses no hazard.
In principle, it must be ensured that the quantity of the escaping substance of the selected system is always below the limit value of the same substance in order to exclude any risk to the employees.
3. testing of the special requirements for filter system for tablet production.
The equipment of the filter system is determined by the determined OEL value of the substances used. The complete process, i.e. the entire personnel and material flow, must be considered: The section with the highest requirements defines the OEB level for all components and thus also the filter system. For substances that are less critical, simpler measures are sufficient than for substances that require a higher classification due to their toxicity.
4. observance of the necessary equipment and maintenance measures of filtration plants.
To ensure process reliability during tablet production, regenerable filter systems are used for the most part for efficient dust removal. In regenerable filter systems, the filter elements are cleaned with compressed air after specified times to counteract premature clogging. This ensures a significant increase in the service life of the filter. As soon as the service life of the filter is reached, i.e. the dust cannot be removed from the filter despite regeneration, it must be replaced. The changeover takes place under appropriate protective measures, which are intended to ensure that the operator and the immediate environment do not come into contact with the substance. For this purpose, various technical containment measures are available for the safe handling of the dedusting system.
The dust blown out of the filter cells during cleaning is collected together with the larger dust particles in a dust collection container. This container must also be changed regularly. As with changing the filter cells, it is just as important here, depending on the composition of the dust, to observe appropriate containment measures so that employee protection remains guaranteed.
5. consideration of the special conditions for dedusting systems in the pharmaceutical industry.
In addition to the health hazard due to the ingredients, there is also the hazard due to the existence of the dust itself: pharmaceutical plants mainly process organic substances. These are generally combustible and ensure that under certain conditions there can be a risk of explosion in the process. Therefore, the filter system must be equipped with the appropriate measures specifically for the respective company requirements. An alternative here are dedusting systems in an explosion-proof design that meet the requirements of the ATEX Directive 2014/34 applicable to these systems.
Conclusion
Modern dedusting systems play a major role in protecting the health of your employees, protecting the environment, and ensuring process reliability in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products. In order to make it easier for all parties involved to select the appropriate dust collection system, thereby ensuring employee protection in the long term, the following criteria should be clarified in advance:
- maximum occupational exposure to dust (OEL)
- Requirements from the pharmaceutical industry
- special requirements for filter system for tablet production
- required equipment and maintenance measures of filter systems
- Special conditions for dedusting systems in the pharmaceutical industry
By following these five criteria, you should be able to select the optimal filtration system for your company’s specific needs, ensuring a virtually dust-free and safe environment for your employees and years of production of your products.


